Cranial Drawer Test
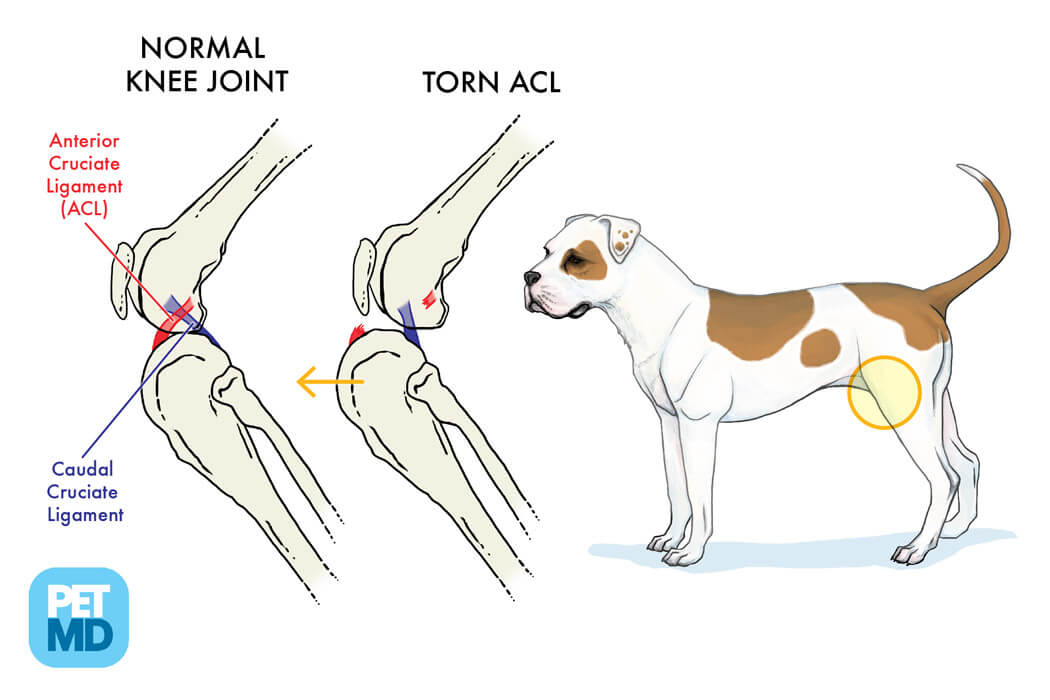
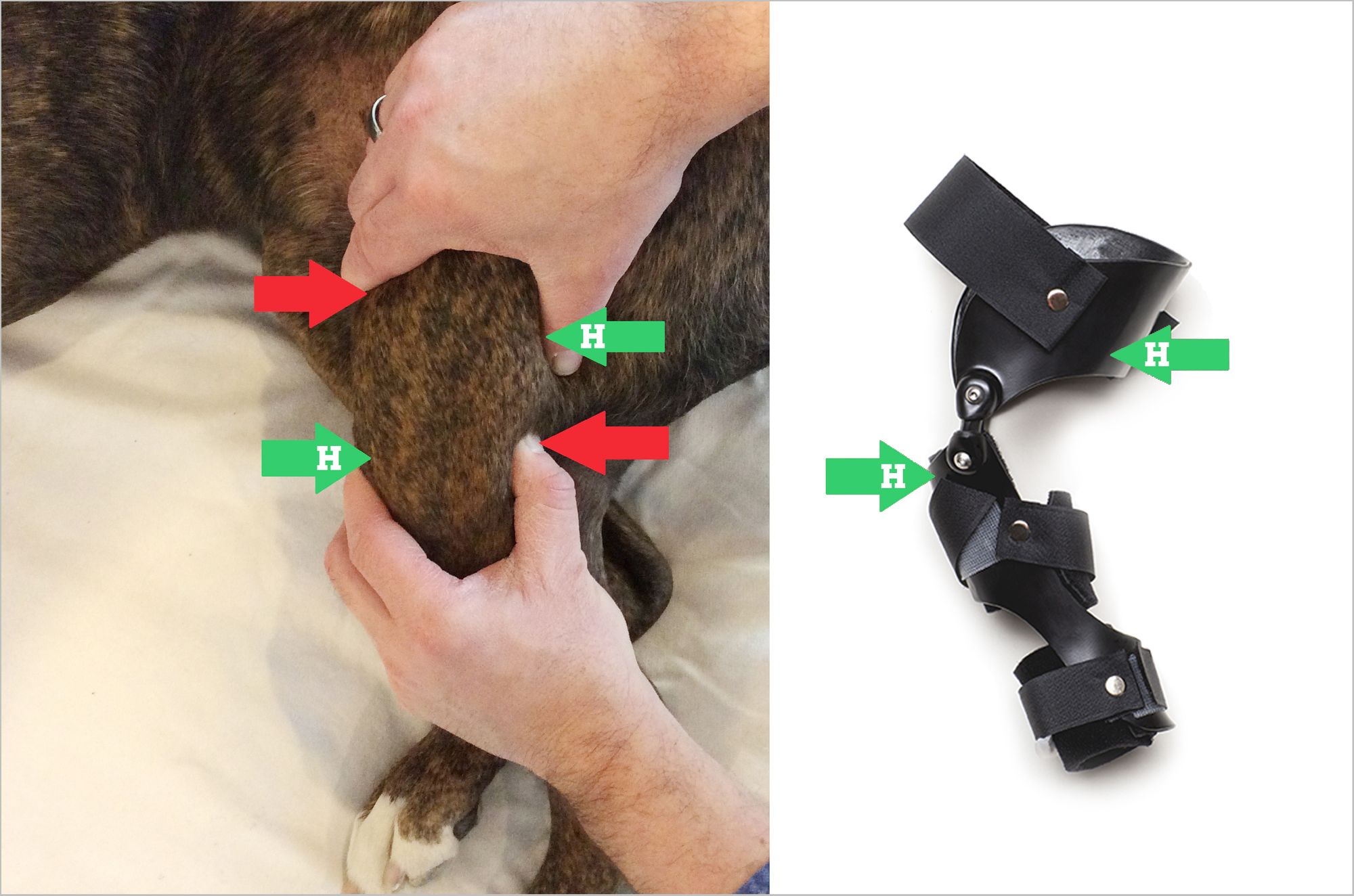
Cranial Drawer Test - Web one of the difficult orthopedic test to learn when you are just starting out as a rehabilitation practitioner or veterinarian is the cranial drawer test.in t. Web during the lameness examination, your veterinarian will try to demonstrate a particular movement, called a cranial or anterior drawer sign. Pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. Web the ccl has 3 main functions: Web craniocaudal translation remains present under passive manipulation (cranial drawer test) and is possible with sufficient anterior shear loading. Web the cranial cruciate ligament helps the stifle (knee) function as a hinge joint. When it ruptures, abnormal movement of the joint occurs, resulting in pain and. Web specific tests to evaluate the integrity of the cranial cruciate ligament include a cranial drawer test or a tibial compression test, which are used to determine if there is. Also called the “cranial drawer test,” this is a passive test for stifle joint instability, which, when positive, means that the cranial cruciate ligament is. Web the hallmark of a ccl rupture is palpation of instability in the stifle joint using the “cranial drawer” and/ or “cranial tibial thrust” tests. Web the cranial drawer test should be done with the leg in flexion and extension, to test both parts of the crcl. In order to feel this, your dog may be placed. Web the ccl has 3 main functions: The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are important for assessing palpable. Web diagnosis diagnosis is made by elicitation of positive cranial drawer or cranial tibial thrust or by palpation of medial buttress.1 medial buttress occurs rapidly after ligament. Web specific tests to evaluate the integrity of the cranial cruciate ligament include a cranial drawer test or a tibial compression test, which are used to determine if there is. In this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior pressure is applied to the. When it ruptures, abnormal movement of the joint occurs, resulting in pain and. Complete tear •partial tear positive drawer with stifle flexed, but not with. If no drawer is palpated, but crcl injury is still. Web the loss of these normal findings indicates periarticular fibrosis, joint effusion or both. Web if it is suspected that your dog has a cranial cruciate ligament tear or rupture, your veterinarian will perform a physical exam to determine whether or not this type of. Web why is crclr underdiagnosed so frequently? In general, radiographic images are used to visualize. Web one of the difficult orthopedic test to learn when you are just starting out as a rehabilitation practitioner or veterinarian is the cranial drawer test.in t. Pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. Web diagnosis of cranial cruciate ligament (ccl) tears is made through a combination of orthopedic. Web the loss of these normal findings indicates periarticular fibrosis, joint effusion or both. Web cranial drawer test landmarks •lateral fabella •patella •tibial tuberosity •fibular head partial vs. Web craniocaudal translation remains present under passive manipulation (cranial drawer test) and is possible with sufficient anterior shear loading. This abnormal forward movement of. Web the ccl has 3 main functions: Veterinary school instruction has traditionally emphasized teaching subtle and difficult manipulative physical examination. In order to feel this, your dog may be placed. Diagnosis is based on the demonstration of a specific test,. (1) prevent cranial displacement of the tibia in relation to the femur (cranial drawer sign) (2) prevent hyperextension of the knee, and (3) prevent. Web definitive diagnosis. When it ruptures, abnormal movement of the joint occurs, resulting in pain and. Web a positive tibial compression test and cranial drawer test confirm cclr. Also called the “cranial drawer test,” this is a passive test for stifle joint instability, which, when positive, means that the cranial cruciate ligament is. Web the ccl has 3 main functions: Complete tear •partial. Diagnosis is based on the demonstration of a specific test,. The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are important for assessing palpable. When it ruptures, abnormal movement of the joint occurs, resulting in pain and. Web the ccl has 3 main functions: Web diagnosis of cranial cruciate ligament (ccl) tears is made through a combination of orthopedic examination findings. Web diagnosis of cranial cruciate ligament rupture is usually made by a positive cranial drawer sign. Pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. Web cranial draw test. Web definitive diagnosis of rupture of the ccl demands an assessment of stifle joint stability by means of the cranial “drawer” test,. Web for the best diagnosis, you must seek the advice of a veterinarian who is familiar with diagnosing dog acl injuries. In order to feel this, your dog may be placed. The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are important for assessing palpable. (1) prevent cranial displacement of the tibia in relation to the femur (cranial drawer sign) (2). Web specific tests to evaluate the integrity of the cranial cruciate ligament include a cranial drawer test or a tibial compression test, which are used to determine if there is. Web the cranial cruciate ligament helps the stifle (knee) function as a hinge joint. When it ruptures, abnormal movement of the joint occurs, resulting in pain and. (1) prevent cranial. Web cranial drawer test landmarks •lateral fabella •patella •tibial tuberosity •fibular head partial vs. This abnormal forward movement of. Web the ccl has 3 main functions: Web why is crclr underdiagnosed so frequently? Diagnosis is based on the demonstration of a specific test,. Also called the “cranial drawer test,” this is a passive test for stifle joint instability, which, when positive, means that the cranial cruciate ligament is. If no drawer is palpated, but crcl injury is still. Web diagnosis of cranial cruciate ligament rupture is usually made by a positive cranial drawer sign. Web cranial draw test. Web one of the difficult orthopedic test to learn when you are just starting out as a rehabilitation practitioner or veterinarian is the cranial drawer test.in t. In order to feel this, your dog may be placed. (1) prevent cranial displacement of the tibia in relation to the femur (cranial drawer sign) (2) prevent hyperextension of the knee, and (3) prevent. Web diagnosis of cranial cruciate ligament (ccl) tears is made through a combination of orthopedic examination findings (eg, positive cranial drawer, cranial tibial translation). Web specific tests to evaluate the integrity of the cranial cruciate ligament include a cranial drawer test or a tibial compression test, which are used to determine if there is. Complete tear •partial tear positive drawer with stifle flexed, but not with. Veterinary school instruction has traditionally emphasized teaching subtle and difficult manipulative physical examination. Web the cranial drawer test should be done with the leg in flexion and extension, to test both parts of the crcl. Web diagnosis diagnosis is made by elicitation of positive cranial drawer or cranial tibial thrust or by palpation of medial buttress.1 medial buttress occurs rapidly after ligament. Web the ccl has 3 main functions: The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are important for assessing palpable. Web the hallmark of a ccl rupture is palpation of instability in the stifle joint using the “cranial drawer” and/ or “cranial tibial thrust” tests.Positive cranial drawer sign in a dog with a cranial (anterior
Cruciate Disease The Cranial Drawer Test YouTube
Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Goals of Cranial Cruciate Ligament
ACL and CCL diagram provided by PetMD
Anterior drawer test for ACL injury... Medicine Notes, Emergency
How to test the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) of the Knee using the
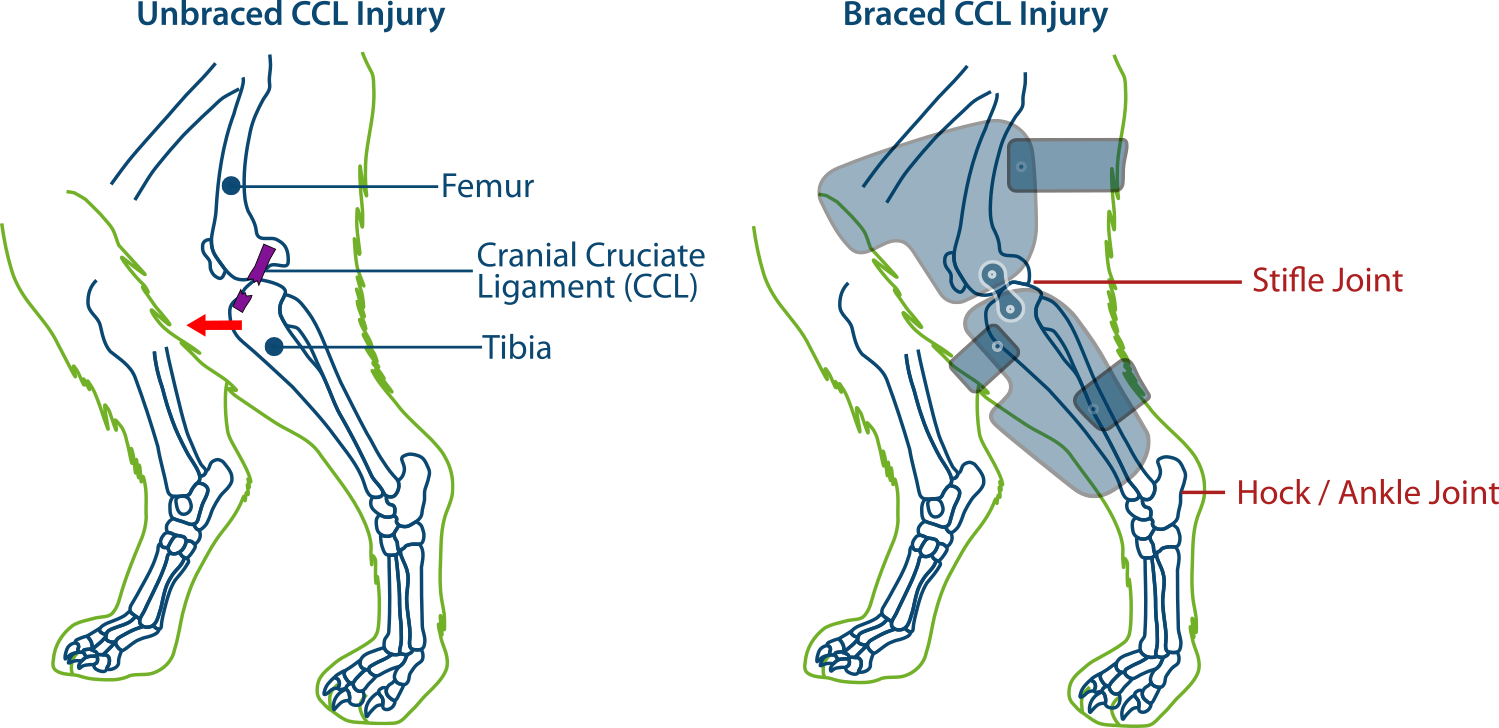
Torn ACL in Dogs How Braces Help
Anterior Drawer Test for ACL How to Perform the Anterior Drawer Test
Drawer Test Bruin Blog
Dog Stifle CCL/ACL Injury Support Brace — PawOpedic
In General, Radiographic Images Are Used To Visualize The Instability Of The Stifle Joint By Tibial.
Diagnosis Is Based On The Demonstration Of A Specific Test,.
Web The Loss Of These Normal Findings Indicates Periarticular Fibrosis, Joint Effusion Or Both.
Web If It Is Suspected That Your Dog Has A Cranial Cruciate Ligament Tear Or Rupture, Your Veterinarian Will Perform A Physical Exam To Determine Whether Or Not This Type Of.
Related Post: